IMPACT ON FRENCH CONSUMERS’ DAILY LIVES
Single-use plastics are found everywhere in our daily lives, including in cosmetic products, so the French Anti-Waste Law is expected to a major impact in consumer’s lives and habits.
The French Anti-Waste Law, also called, AGEC Law (Loi relative à la lute contre le gaspillage et a l’économie circulaire), contains about 50 measures that include new obligations (requirement of transparency), new prohibitions (control of irreversible ecological ambitions) and new tools to better control and sanction offences against the environment. These will have a huge impact on the production method of companies and the consumption pattern of citizens.
Phasing-out disposable plastic, better informing consumers, fighting against waste and promote reuse, acting against planned obsolescence and better producing are main pillars of the AGEC law.
The law lays down a progressive and reasoned method for phasing out by laying down 5-year plans which will provide for plastic reduction, reuse and recycling targets. The main goal is to achieve zero disposable plastic by 2040 and this ban will happen in 4 stages (2020-2025, 2025-2030, 2030-2035 and 2035-2040).
COSMETICS MADE AVAILABLE ON THE FRENCH MARKET
Cosmetic and personal care products that are made available on the French market need also to comply with Anti-Waste law.
This law strictly prohibits the destruction (landfilling and incineration) of unsold non-food products (which includes cosmetics) and companies will now be required to give them a use (e.g., donating them to associations, or recycle). However, there is an exception for products for which recycling would lead to a negative environmental impact or if it is prohibited (because it poses a risk to the environment or human health) or for which no technical solution for reuse, recovery or recycling exists.
Other requirement is that consumers need to be well informed, including on the environmental characteristics of the products. In this way, the Triman Logo is mandatory and shall be indicated on the product, its packaging or on the documentation provided with the product. This legal obligation also applies to products sold online to France. It needs to be accompanied by the information on the sorting process for each type of product. Any other signs that might confuse consumers regarding the sorting rules should be removed.
This logo means that the waste is subject to a sorting rule and it does not mean that the waste will necessarily go in the recycling bin (e.g. yellow waste bin for packaging, at-store return/take-back for electric and electronic equipment, specific collection stations for batteries, etc.) .
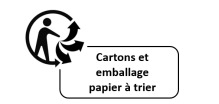
The Triman Logo should be printed in black and white, with a minimum size of 6 mm, and it can not be superimposed by other visual elements or be smaller than symbols printed alongside it. The information regarding the material and the sorting process needs to be in French (including on e-commerce), as this is a specific obligation for the French market.
A transition period was granted until 9 March 2023, for packaging produced or imported before 9 September 2022.
Being the first in the world, the French Anti-Waste Law is considered a groundbreaking law and a crucial step towards a better protection of the environment. For more information, do not hesitate to contact us at info@criticalcatalyst.com.
References:
1. LOI nº 2020-105 du 10 février 2020 relative à la lutte contre le gaspillage et à l’économie circulaire. Journal Officiel de La République Française. 11 février 2020.
2. Ministére de la Tansition Écologique Et Solidaire – The Anti-Waste Law in the Daily Lives of the French People, What Does That Mean in Practice?















